HL7 Interface Standards Continue to Power Healthcare Data Sharing
“The report of my death was an exaggeration.” – HL7v2. Wait. That was actually Mark Twain in a letter to a New York reporter. But it also applies to the Health Level 7 (HL7) healthcare interface standard.
The fact is, HL7v2 remains the most widely used healthcare interface standard by a large margin. HL7.org tells us that:
- 95% of U.S. healthcare organizations use HL7v2 interface standards
- More than 35 countries have HL7 interface implementations
So while the most excited healthcare interoperability buzz focuses on FHIR (itself an HL7 evolution), the HL7 interface standard powers most current data sharing in healthcare.
Let’s take a closer look at the HL7 interface standard and how your organization can advance interoperability with existing HL7 implementations while balancing other data exchange capabilities and future technologies.
What Are HL7 Interfaces?
Health Level Seven (HL7) is a set of international standards that involves the exchange of data among healthcare providers.
An HL7 interface is an API (Application Programming Interface), offering a standardized interface for healthcare systems to communicate through HL7 messaging standards. It serves as a translator between diverse systems, streamlining the connection of healthcare applications to forge secure, robust communication channels.
Quick History of the HL7 Interface Standard
In the early 1980s, physicians and providers “interoperated” with phone calls, faxes, and paper forms. Many healthcare software vendors built expensive individual interfaces to exchange data with other individual healthcare systems and data sources. These interfaces took tons of work to build and maintain but created just one closed data-sharing tunnel at a time.
Health Level 7 International set out to fix things. The nonprofit organization was formed in 1987 with a mission to create harmony and common data interface standards for rapidly growing EHR and healthcare information technologies. The idea: Common interface standards and data formats would reconcile the unwieldy, disconnected universe of EHRs and other health data to accelerate integration and improve care and outcomes.
Over time the HL7 interface standards have largely succeeded in helping healthcare providers and technology organizations:
- Ensure uniform EHR data for a consistent, complete patient view
- Automate workflows by reducing and eliminating manual data entry
- Help exchange health reporting electronically with regulators
- Open digital health records and data access for patients
- Reduce investments in new technology upgrades by building on a common standard
What Are the Benefits of Using HL7?
HL7 plays a key role in facilitating every aspect of data exchange to increase efficiency and decrease errors. Here are some benefits of HL7 utilization in healthcare:
- Data uniformity and interoperability
- Clearer interpretation
- Workflow automation increase
- Constant maintenance and upgrades
- Regulatory compliance simplification
1. Data Uniformity and Interoperability
Establishing a standard data exchange process enables healthcare providers to easily retrieve and share patient records across systems such as EMR (Electronic Medical Record), RIS (Radiology Information System), LIS (Laboratory Information System), etc, eliminating redundancy and ensuring accuracy.
The HL7 Interface boosts data exchange efficiency and patient care by offering a holistic clinical perspective.
With more patient records accessible, clinicians can quickly access relevant data for immediate medical attention. Improved data consistency and interoperability support informed decision-making, enhancing patient outcomes organization-wide.
2. Clearer Interpretation
Standardizing the format and language of health records through HL7 reduces the risk of misinterpretation from different data systems. This unified approach allows clinicians and healthcare professionals to access a coherent view of patient records, leading to well-informed clinical decisions and improved patient outcomes.
Moreover, HL7 standards streamline the integration of new technologies into current systems, cutting down both the cost and time needed for implementation.
3. Workflow Automation Increase
The HL7 Interface streamlines data entry through automation, enhancing workflow efficiency, productivity, and accuracy. By automating tasks, valuable time is freed up for essential duties like patient care and strategic planning. This interface empowers healthcare providers to refine their core operations and boost performance, productivity, and engagement in the long run.
4. Constant Maintenance and Upgrades
By adopting HL7 with its continuous improvement framework, healthcare institutions can remain updated to remain compliant with the latest regulations. This ongoing maintenance helps to address any emerging security vulnerabilities, thereby safeguarding patient data against breaches.
Furthermore, the use of HL7 standards facilitates easier integration of new technologies and software into existing systems. HL7 provides a consistent method for incorporating updates, which ensures that healthcare providers have access to the latest tools and information.
5. Regulatory Compliance Simplification
By facilitating the electronic sharing of data between healthcare providers and regulators, the HL7 Interface guarantees seamless adherence to public health reporting standards and regulatory requirements.
HL7 Interface alleviates administrative pressures on healthcare institutions, enabling them to concentrate on providing high-quality patient care.
REF:
https://www.citetech.com/learn/everything-you-need-to-know-about-hl7-interfaces
https://www.intely.io/blog/the-benefits-of-using-intelys-hl7-interfaces
HL7 Interface Versions and Releases
Here’s a quick summary of major HL7 versions and releases:

HL7v1
HL7 published the draft, proof-of-concept version 1 standard in 1987. It mapped out the overall structure of the interfaces, ADT, order entry, and display-oriented queries. The organization used the standard for demonstrations, operational experience, and industry input. The HL7 team did not intend to seek accreditation or production implementation for HL7v1.
HL7v2
Things got real with HL7v2. HL7 released version 2.0 in October 1988, the first release that saw limited production. The most current release is HL7v2.9, with a few sub-releases along the way. Notably, each iterative 2.x release is compatible with previous ones.

HL7v2 introduced key interoperability advances:
- Support of most common global healthcare interfaces
- A framework for accommodating things that are not part of the standard
- Lower implementation costs
Most HL7 message exchanges today use the specifications in versions 2.3 and 2.31.
HL7v3
First released in 2005, the HL7v3 interface standard was an entirely new, more precise standard meant to increase adoption, define a consistent data model, and avoid legacy issues. For reasons we’ll discuss further below, the industry has resisted the adoption of the now largely irrelevant HL7v3 interface standard.
The Interoperability Path Forward: HL7v2, HL7v3, and FHIR
These questions and answers clarify the sometimes bumpy progression forward from the popular HL7v2 interface standard:

Why Not Just Stick with HL7v2 Interface?
HL7v2 is ubiquitous and successful. Why can’t healthcare settle on it as the interface and integration standard of the future?
As much as HL7v2 has advanced interoperability, it has several limitations:
- It can be hard to implement.
- It only handles structured data, not unstructured data such as images and static documents.
- Developers have a steep learning curve with HL7v2 as they are more familiar with REST, JSON, XML, and other web-based tools and technologies.
- The HL7 pre-web technology foundation has reached its ceiling for advancement.
HL7v2 has and will continue to do a lot of interoperability heavy lifting in healthcare. But it’s not the direction for the future.
Why Did HL7v3 Interface Stumble?
HL7v3 promised to improve the limitations of HL7v2 data modeling and standards variation. Its good intentions hit some significant stumbling blocks:
- I was not backward compatible with HL7v2, which meant organizations had to implement and maintain v3 solutions alongside existing v2 solutions.
- Version 3 interfaces typically could not communicate with v2 interfaces.
- It is complex and difficult to implement with too little return for the effort.
Advance to HL7 FHIR—What Interface Gaps Does FHIR Close?
As HL7v3 stalled, innovators on the HL7 team shifted to a future vision: Incorporate widely used web standards and protocols such as REST, JSON, and XML to make interface development and implementation easier. That became the FHIR standard, first released in 2014.
FHIR has advanced three critical components of healthcare data interoperability that previous interface standards could not address:
- Solve Unstructured Data Exchange: FHIR lets systems share structured and unstructured data, closing the most critical interoperability gap.
- Build Interfaces Faster and Easier: Developers have more experience with more modern API technologies (RESTful protocol, choice of JSON, XML, or RDF for representing data), making FHIR interface standards easier to learn and APIs easier to develop and implement.
- Introduce Resources to Make Better, More Intuitive Sense of Data: The FHIR interface standard introduced resources, data categories that represent concepts such as patients, lab results, insurance claims, appointments, and more to make interfaces more flexible and development more intuitive.
And the 21st Century Cures Act and final rules from the Centers for Medicare Services (CMS) now mandate FHIR interface adoption by most every healthcare organization. We have and will continue to educate and guide success in EHR integration and data sharing with FHIR.
How to Choose the Right HL7 Integration Approach?
Choosing the appropriate HL7 integration strategy requires a thorough assessment of the organization’s needs, current systems, and compatibility prerequisites. By thoughtfully evaluating these aspects, healthcare institutions can identify the optimal solution for their HL7 interface integration or implementation.
Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of point-to-point interfaces versus HL7 integration engines. For intricate integrations or sizable organizations, an EHR interoperability engine may provide greater scalability and flexibility.
Seeking advice from HL7 integration specialists can offer invaluable support in navigating this pivotal choice, guaranteeing that the selected approach harmonizes with the organization’s objectives and needs.
KMS Healthcare: Make HL7 Part of Your Harmonious Integration Model
Even with FHIR and other future technology options, HL7 will remain a cornerstone of healthcare interoperability for years or even decades to come. Other interface and data sharing formats also comprise an additional important part of the healthcare integration mix for most organizations, including EDI, flat files, web services, and continuity of care records (CCRs). And there are many other use-specific interface and message formats for imaging, pharmaceuticals, labs, orders, and other healthcare events and information.
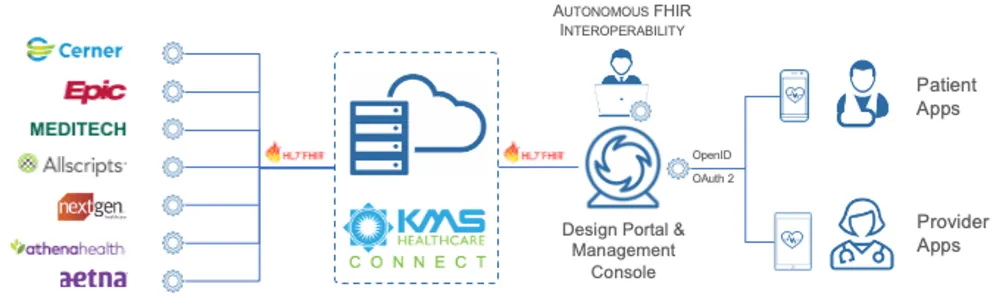
That’s why you need a technology partner with elite experience and understanding of the entire healthcare integration universe, including HL7.
That’s KMS Healthcare. Partner with us to establish a harmonious integration model to get the most valuable, productive real-time data sharing across all of your systems.
Partner with KMS Healthcare to:
- Determine everywhere in your IT landscape that HL7 interfaces power integration
- Develop strategies and apply tools to test and tune your existing HL7 integration points
- Get the right, consistent, and comprehensive EHR data to patients, doctors, payers, and billers
- Forge a strong strategy for incorporating FHIR and SMART on FHIR technologies
- Start implementing FHIR APIs rapidly and strategically with KMS Connect
- Stay ahead of CMS deadlines for FHIR and SMART on FHIR adoption and compliance
- Assess, test, and tune other critical data exchange systems and formats across your organization, including EDI, flat file exchange, web services, and more.
Speak a shared language among health data systems, wearables and other remote devices, claims systems, patient-provided data and ePRo, patient portals, and every point of care and communication across the patient journey. Establish confident optimum integration performance today and a smart, smooth path forward to better and better interoperability in the future.

Click to start your path to integration harmony with KMS Healthcare…