Healthcare providers collect mountains of data about patients, clinical activities, claims and billing, and population health and trends. To handle this information explosion, healthcare organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to ensure seamless integration of healthcare data and services.
Healthcare data integration plays a crucial role in modern healthcare delivery by enabling providers to access comprehensive patient records, share information, and collaborate effectively. Healthcare organizations encounter common challenges when implementing healthcare data integration systems.
Let’s examine those challenges and practical strategies to overcome hurdles and navigate successful healthcare data integration.
What is a Healthcare Data Integration System?
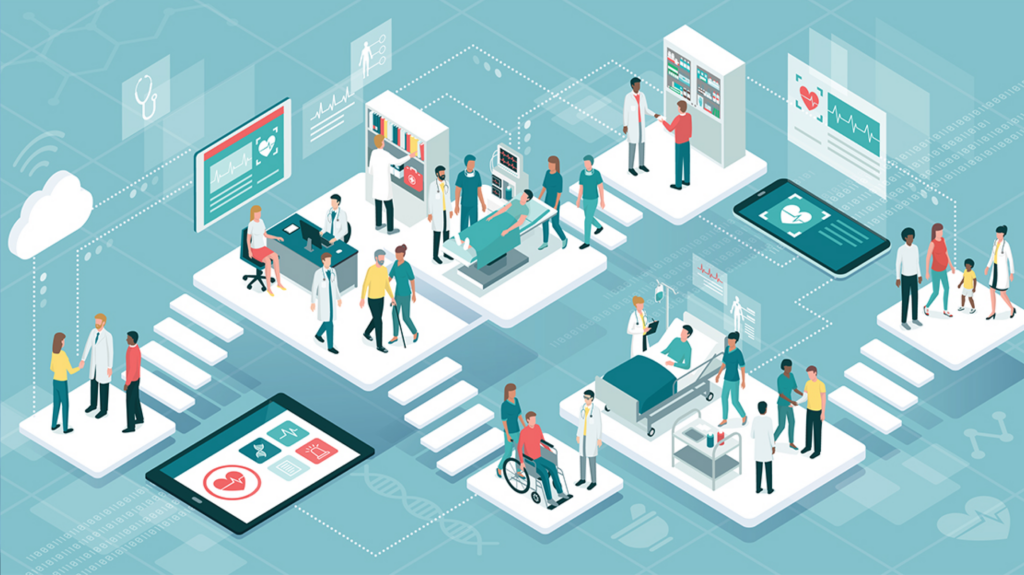

Healthcare data integration enables collaborative utilization of data across different systems, such as electronic health records (EHR), lab, billing, and administrative systems. Healthcare data integration enables the seamless exchange of patient, clinical, and managerial data across various healthcare applications and systems.
Healthcare data integration creates a complete view of a patient’s medical history, aiding informed decisions for better care. Connected healthcare system integration enables effective communication, enhanced interoperability, and patient data exchange.
Here are a few common examples of healthcare systems integration:
- Electronic health information exchange (HIE): HIE systems enable healthcare providers and organizations to securely share patient data, improving care coordination and timely access to vital information.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems digitize and centralize patients’ medical information. These real-time, patient-centered records go beyond traditional clinical data, incorporating key administrative details, progress notes, medications, and more.
- Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS): A PACS helps manage medical images such as X-rays and MRIs. It allows healthcare professionals to digitally access and share these images for quicker diagnoses and treatment planning.
Key Considerations for Effective Healthcare Data Integration
Several things drive efficiency and effectiveness in integrated healthcare data systems, ensuring accurate data, privacy, and seamless information exchange for healthcare data integration.
- Data Standards: Standardized formats and protocols for healthcare data ensure consistency and compatibility among integrated systems, enabling seamless data sharing and communication.
- HIE Infrastructure: HIE infrastructure facilitates the secure exchange of patient information among various healthcare providers, organizations, and systems. It forms the backbone of integrated healthcare.
- Master Patient Index (MPI): MPI is a healthcare database that maintains a unique identifier for each patient, enabling accurate patient matching and record linking across different healthcare systems. This ensures that the right information is associated with the correct patient.
- Consent Management: Consent management tools and processes allow patients to control who can access their health data. This component is vital for ensuring patient privacy and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Healthcare integration systems provide healthcare professionals with quick access to a patient’s complete medical history, enabling more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Navigating Common Challenges in Implementing Healthcare Data Integration Systems

Integrating data in healthcare presents challenges.
Healthcare data comes from many sources, from conventional clinical documents to the 24/7 data uploads from wearable devices. It empowers individuals to take charge of their health, but it also generates an abundance of data, raising concerns about interoperability and privacy. Moreover, healthcare organizations with limited technological resources face the challenge of budget planning and selecting IT vendors that best align with their technical requirements.
Below is a list of common challenges organizations face when implementing healthcare integration systems, with practical advice.
1. Interoperability Issues
Interoperability matters most in healthcare data integration to ensure a smooth transition and seamless exchange.
a. Lack of Standardization:
Healthcare systems often use varied data formats and communication protocols, creating difficulties in smooth information exchange. The lack of standardized data models and consistent terminology can result in misinterpretation and errors when transferring data.
b. Different Data Formats
Variability in data formats and communication protocols across different healthcare systems hinders smooth data exchange and integration. Systems might use different coding systems, leading to translation errors and data loss.
In healthcare data integration, it is crucial to establish and promote standardized practices, protocols, and formats for sharing healthcare data among systems.
There are several key standards in the healthcare system that must be strictly adhered to:
- HL7 is a widely known standard for exchanging healthcare data globally. It consists of protocols, messaging standards, and data formats to make exchanging structured information easier. Adhering to HL7 ensures healthcare data is consistently understood and interpreted.
- Fast Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is a modern standard for exchanging electronic healthcare data. It’s straightforward, adaptable, and user-friendly. FHIR employs a RESTful API approach, making it great for web and mobile health apps. Adopting FHIR encourages standardized data formats and simplifies integration.
- SMART on FHIR is an open platform for healthcare apps to securely integrate with electronic health record (EHR) systems. It enables third-party apps to interact seamlessly, promoting interoperability and extending healthcare functionality.
By embracing these standards, healthcare organizations can streamline data sharing, enhance care coordination, and adapt to evolving healthcare requirements.
2. Security Concerns
In healthcare integration, ensuring security is crucial to safeguard patient data and maintain trust. Two primary security considerations in healthcare integration include:
a. Data Privacy and Compliance
Healthcare organizations manage sensitive patient data, including medical records, billing info, and personal identifiers. Protecting the privacy and confidentiality of this data is a legal and ethical duty. Non-compliance with regulations like HIPAA can lead to severe consequences, such as legal penalties and reputation damage.
b. Cybersecurity Threats
The digitalization and connectivity of healthcare data systems present a risk of cyberattacks. Threats such as ransomware and data breaches can jeopardize patient privacy, disrupt operations, and result in financial losses.
Consider taking effective data security measures in healthcare integration:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data can safeguard sensitive healthcare information during transmission and storage. This ensures protection from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- HIPAA Compliance: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes crucial privacy and security standards for healthcare information. All healthcare organizations must adhere to HIPAA regulations.
- Routine Audit: Perform regular security audits to identify and address emerging threats. Keep software and data encryption methods up-to-date for optimal protection.
Healthcare organizations can strengthen data security, maintain regulatory compliance, and protect patient privacy in their data integration systems by implementing these measures.
3. Budget Constraints and Effective Planning
It is imperative to consider the main expenses related to healthcare data integration and anticipate any supplementary costs associated with system upkeep and monitoring.
a. Cost of Implementation
Implementing healthcare data integration systems involves significant upfront costs, including software, hardware, training, and services.
b. Ongoing Maintenance Expenses
Healthcare integration systems require ongoing maintenance, including software updates, system monitoring, technical support, and staff training. These recurring expenses can strain operational budgets.
To tackle these challenges, consider the following steps:
- Long-term financial planning: Healthcare organizations engage in long-term financial planning by allocating funds to meet data integration needs. This proactive approach ensures appropriate budgeting for ongoing expenses.
- Agile budgeting: Enable healthcare organizations to adjust based on shifting priorities and emerging data integration requirements. This flexibility allows for the allocation of resources where they are most needed.
- For companies that lack technological resources and want to minimize the expense of hiring in-house tech talent, outsourcing to a healthcare technology development company like KMS Healthcare can reduce internal staffing costs and take advantage of superior technical expertise.
4. Choosing The Right IT Vendor
a. Finding the Right Healthcare Data Integration Solution Provider
Healthcare organizations encounter complex data integration demands due to the range of systems, data formats, and regulations. Selecting a vendor that aligns with their needs, goals, and values is crucial to ensure seamless operations, avoid integration challenges, and prevent dissatisfaction. Making an informed decision is essential. Choosing the right vendor can also be a daunting task. Here are some expectations to consider when selecting healthcare IT vendors.:
1. Compatibility with Existing Systems
- Assess whether the vendor’s technology seamlessly fits within your current ecosystem.
- Ensure their solutions work well with other systems and technologies.
2. Technical Capabilities
- Evaluate the vendor’s EHR system for its integration capabilities with other products like practice management systems, billing software, and public health databases.
- Look into the technical features and capabilities of the EHR system to ensure it meets your operational needs.
3. Interoperability and Standards
- Examine how well the vendor’s EHR system aligns with industry standards and interoperability protocols.
- Ensure that their system adheres to data privacy regulations such as HIPAA and offers encryption and access controls.
4. Support and Maintenance
- Expect reliable technical support from the vendor.
- Ensure they offer timely assistance in case of issues, regular updates, patches, and a dedicated support team to address your concerns.
5. Cost and Budget
- Consider the overall cost and how it fits within your budget.
- Look for pricing structures that align with your financial plan.
- Use budget tools to enhance cost efficiency.

6. Collaboration and Communication
- Assess the vendor’s ability to collaborate and communicate effectively with your team.
- Ensure they understand your organization’s goals and can work cohesively to achieve them.
b. Vendor Lock-In Risks
Vendor lock-in happens when healthcare organizations rely too much on a specific vendor’s technology or solutions. This can limit flexibility, slow down innovation, and cause costs to go up in the long run.
To reduce the dangers of vendor lock-in in healthcare IT, organizations should prioritize vendors that focus on interoperability, data integration, open APIs, and adherence to industry standards. Choose scalable solutions and create strategies for potential vendor changes. Stay updated on new technologies and negotiate flexible contracts with periodic reviews.
To handle these risks and meet your needs, it’s wise to select a trustworthy healthcare data integration provider. Find a partner that is dedicated to keeping your organization adaptable.
Introducing KMS Healthcare for your Integration Solutions
KMS Healthcare is your dependable partner for healthcare data integration solutions. As a trusted software development collaborator, we aim to help you overcome data integration challenges, bridge technology gaps, and enable seamless implementation and maintenance of your healthcare integration systems.
KMS Healthcare tackles the complexity of healthcare data integration by aligning our solutions, tailor-made for your needs and goals. We ensure compliance with industry standards and data privacy regulations with exceptional support on your projects.
With over 14 years of healthcare technology experience and a proven track record of success with 50+ top U.S. clients, we offer approaches emphasizing open standards, interoperability, and modular solutions. This reduces the risk of being tied to a single vendor while enhancing your healthcare integration capabilities.

Join us on this journey. Schedule a consultation with our expert team at KMS Healthcare, and let us help you navigate the complexities of healthcare data integration.