Telemedicine has grown exponentially in recent years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for accessible healthcare solutions. The global telemedicine market was valued at USD 97.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 107.52 billion in 2024, ultimately growing to USD 432.31 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.0%.
Telemedicine offers significant benefits by connecting patients with physicians remotely, reducing healthcare costs, and improving access to care. These advantages have led to widespread adoption among hospitals and physicians, while governments worldwide are implementing supportive regulations and reimbursement policies to promote telehealth initiatives.
Let’s explore the top 5 telemedicine devices transforming patient care and redefining modern healthcare.
What are Telemedicine Devices?
Telemedicine devices are specialized tools that leverage telecommunications technology to deliver healthcare services remotely. While basic resources such as phones and internet connections form the foundation, many telemedicine systems rely on advanced equipment to enhance the quality of care.
Types of Telemedicine
- Real-time telemedicine: Live consultations conducted through video conferencing platforms for immediate patient-provider interaction.
- Store-and-forward telemedicine: Sharing medical data like images and test results via secure communication channels for later expert review.
Hospital telemedicine carts with integrated cameras, monitors, and diagnostic tools facilitate remote data capture and seamless transmission for effective healthcare services.
The Importance of Telemedicine Devices
Telemedicine devices are transforming healthcare, particularly in underserved or rural areas with limited access to healthcare professionals. Remote consultations and continuous monitoring allow healthcare providers to extend their reach, improving care for patients with chronic conditions and reducing hospital re-admissions.
Telemedicine devices also enhance the quality of care by enabling specialists to review medical data and provide consultations remotely. Patients can avoid long-distance travel, saving time and money, while receiving accurate, timely diagnoses. Overall, telemedicine increases patient care efficiency, fosters better communication, and eases the burden on healthcare systems.
What are the Components of Telemedicine Devices?
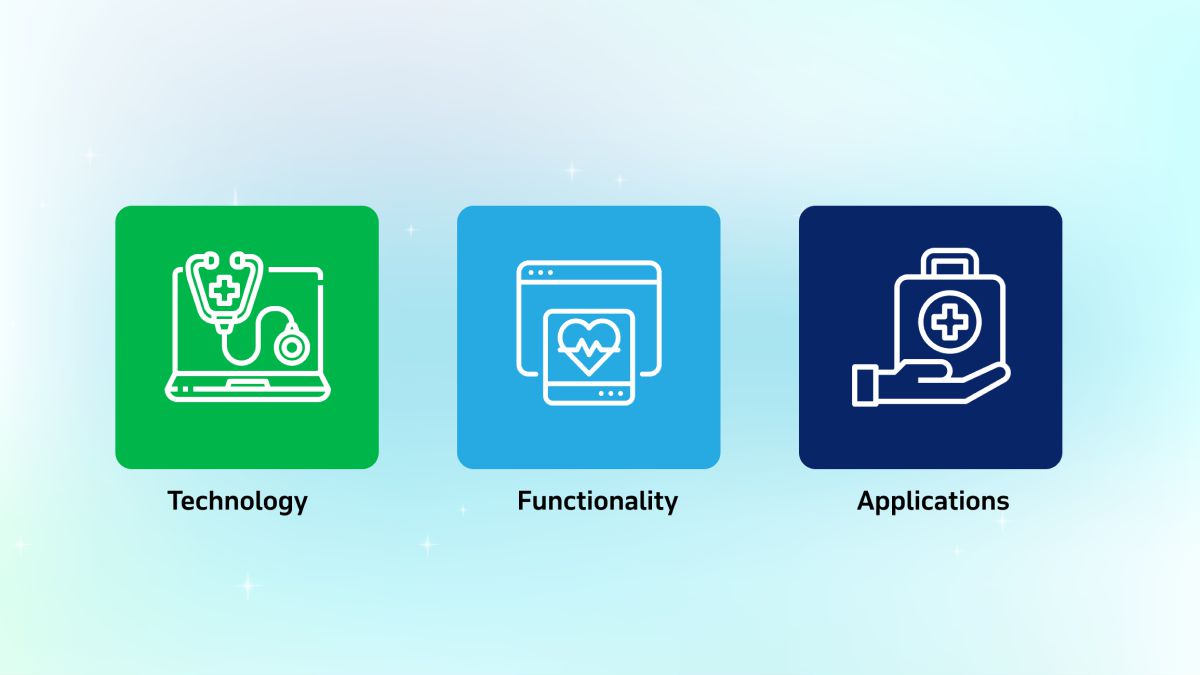
Telemedicine devices are comprised of various essential components that work together to enable remote healthcare services, ensuring seamless communication, accurate diagnoses, and effective patient management:
Component | Applications |
Technology | Synchronicity: Real-time interactions, including video conferencing, ensure immediate communication between patients and healthcare providers. |
Network Design: Telemetry systems and remote sensing tools capture and relay patient data directly to healthcare professionals for timely analysis. | |
Connectivity: Stable wired or wireless connections enable seamless remote consultations and data exchanges. | |
Functionality | Consultation: Direct virtual connections allow patients to receive expert advice from specialists on health concerns. |
Diagnosis: Medical data or images shared through secure channels support accurate diagnosis of conditions remotely. | |
Mentoring & Monitoring: Ongoing guidance and continuous health tracking ensure effective disease management and adherence to treatment plans. | |
Applications | Medical Specialty: Platforms support various specialties, including cardiology, dermatology, and mental health. |
Disease Entity: Tailored tools focus on managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. | |
Site of Care: Virtual care is accessible from homes, clinics, or hospitals, offering flexibility in healthcare delivery. | |
Treatment Modality: Solutions enhance treatments through video consultations, monitoring devices, and follow-up care tools. |
5 Common Telemedicine Devices
Here’s a quick look at the most common telemedicine devices that healthcare providers rely on to deliver effective remote care.
1. Telemedicine Carts
Telemedicine carts are mobile stations equipped with essential tools like cameras, monitors, and medical devices. These carts facilitate seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers in different locations. By integrating diagnostic tools, the carts enable on-the-spot examinations and improve the efficiency of consultations in healthcare facilities.
In hospitals, telemedicine carts enhance workflow by allowing providers to conduct virtual consultations without moving patients. In some cases, home-based telemedicine carts support ongoing care, especially for individuals with limited mobility.
2. Telemedicine Kiosks
Telemedicine kiosks are standalone units designed for remote consultations in retail clinics, workplaces, or community hubs. These kiosks typically include high-resolution cameras, medical devices for basic vitals, and secure communication systems. Patients can step into the kiosk for a private consultation, making healthcare more accessible.
Organizations investing in kiosks prioritize employee or community health by offering convenient care options. Despite higher initial costs, kiosks are valuable for reducing wait times and enhancing access to expert medical advice.
3. Digital Cameras for Telemedicine
Specialized digital cameras capture high-quality images and videos for diagnostic purposes. Some devices are engineered for detailed views, such as internal ear examinations or skin evaluations. These cameras transmit medical images to specialists, enabling accurate remote diagnoses.
High-resolution imaging is particularly important in dermatology, ENT, and ophthalmology. Advanced cameras contribute to effective store-and-forward solutions, where images are reviewed asynchronously by medical experts.
4. Telemedicine Kits
Portable telemedicine kits support healthcare providers in remote or underserved areas. Kits often include a small computer, a camera, and basic diagnostic tools like stethoscopes or otoscopes. The durable design ensures reliability in challenging environments.
These kits are vital for emergency care or disaster response, where access to traditional facilities is limited. Compact, all-in-one kits empower clinicians to deliver critical care efficiently in diverse settings.
5. Mobile Medical Devices
Mobile medical devices monitor patient health and transmit real-time data to healthcare providers. Examples include ECG monitors, glucose meters, and vital signs trackers. Advanced versions integrate with telemedicine platforms, enabling continuous patient management.
Devices like digital stethoscopes and handheld ultrasound systems enhance remote diagnostics. Mobile technology allows personalized care and helps manage chronic conditions more effectively.
Benefits of Telemedicine Devices
Telemedicine devices are reshaping healthcare by addressing critical challenges in patient care, accessibility, cost efficiency, and service delivery, making it easier to provide effective and timely care. Key benefits include:
1. Improved Patient Care
Telemedicine devices enhance patient outcomes through consistent remote monitoring, which helps detect early health issues and reduces re-admissions and mortality rates. Regular virtual consultations strengthen patient-provider relationships, ensuring better communication and adherence to treatment plans. The convenience of remote care increases patient satisfaction by eliminating travel and reducing wait times.
By providing proactive monitoring and improving accessibility, telemedicine helps deliver more personalized care. Patients are empowered to engage more actively in managing their health, strengthening their relationship with healthcare providers.
2. Expanded Access to Healthcare
Telemedicine devices eliminate geographical barriers, bringing healthcare services to rural and underserved communities where access to providers is limited. Patients with mobility challenges benefit from reduced travel, ensuring timely medical attention without physical strain. The flexibility of virtual care allows for faster and more frequent access to health services.
By making healthcare more inclusive, telemedicine reduces disparities and ensures that even hard-to-reach populations receive essential care.
3. Lower Healthcare Expenses
Although telemedicine devices require an upfront investment, they reduce long-term costs by minimizing the need for in-person visits and enabling efficient virtual consultations. Providers save on operational costs, including overhead expenses, while patients avoid travel and time-related costs.
As a result, financial efficiency is improved, making healthcare more affordable and sustainable for both healthcare organizations and patients over time.
4. Streamlined Administration and Scheduling
Telemedicine platforms simplify scheduling, reducing wait times for patients and optimizing providers’ time. Overcoming geographical and time barriers improves resource allocation, allowing clinics to handle more patients efficiently.
Administrative tasks, such as documentation and follow-ups, become more automated, enabling healthcare staff to focus on delivering care rather than managing logistics.
5. Increased Revenue and Broader Services
Telemedicine devices expand a provider’s reach by enabling care for more patients, increasing revenue potential. Services like remote monitoring and virtual screenings open new revenue streams without significant infrastructure investments.
Healthcare organizations can expand their range of services and improve patient satisfaction by offering more flexible care options, ultimately increasing both service capacity and revenue.

How to Choose the Right Telemedicine Devices?
Here are some of the key considerations to keep in mind when researching and implementing telemedicine devices:
1. Matching Functionality for Care Requirements
When choosing telemedicine devices, selecting those that align with the specific healthcare services provided is crucial. For virtual consultations, high-quality video conferencing tools are necessary, while remote monitoring of chronic conditions requires specialized devices like heart rate monitors or glucose meters. Devices must also integrate with existing healthcare systems to manage patient data securely.
By selecting devices that match the specific care requirements, healthcare providers can ensure more efficient and effective service delivery. Devices designed for the intended purpose improve patient outcomes and streamline workflows for healthcare professionals, ensuring a smooth telemedicine experience.
2. Ease of Use and Integration
User-friendly telemedicine devices minimize the learning curve for both healthcare providers and patients, reducing the chances of errors. Devices with intuitive interfaces allow professionals to focus on delivering care rather than troubleshooting technology. Additionally, seamless integration with existing healthcare systems, such as electronic health records (EHR), simplifies processes and ensures consistent service delivery.
Choosing devices that prioritize ease of use and integration leads to better operational efficiency, ensuring telemedicine services are scalable and sustainable, facilitating long-term success for healthcare organizations.
3. Reliability and Quality of Audio/Visual Features
Reliable audio and video are essential for telemedicine devices to ensure clear communication and accurate diagnostics. Devices should provide high-definition video and clear audio without disruptions. Additionally, they must perform consistently throughout consultations to prevent technical issues. Ensuring compliance with security standards, such as HIPAA, is also crucial to safeguard patient data during remote consultations.
Selecting devices with stable performance and high-quality audio/visual features enhances the professionalism of virtual consultations. Clear communication improves patient trust and satisfaction, making telehealth services more effective and dependable.
4. Cost and Long-Term Expenses
While the initial cost of telemedicine devices is a key consideration, it’s also important to evaluate ongoing expenses, including maintenance, software updates, and support services. Choosing cost-effective devices that don’t compromise on quality helps healthcare organizations avoid financial strain while maintaining service standards. Reducing long-term operational costs ensures that healthcare providers can sustain quality care over time.
For a more informed decision, leverage our Cost of Engineering Calculator to compare pricing and value between potential partners. Affordable yet reliable devices maximize healthcare impact without compromising service quality. Proper planning supports scalable telemedicine systems for future expansion.
5. Security and Privacy Compliance
Ensuring that telemedicine devices comply with privacy regulations, such as HIPAA, is essential for protecting sensitive patient information. Devices must feature robust encryption and secure data storage to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Compliance with these security standards maintains patient trust and ensures legal and ethical use of telemedicine services.
Prioritizing security and privacy in telemedicine devices reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures that healthcare organizations adhere to regulatory requirements. Strong security measures foster patient confidence and support ethical practices in remote healthcare delivery.
Read more: Outsourcing Healthcare Software Development: The Complete Guide for Doing It
Challenges of Implementing Telemedicine Devices
Telemedicine devices offer significant potential to enhance healthcare access, reduce costs, and improve the management of chronic conditions. However, several challenges must be overcome to ensure their effective implementation.
Despite its advantages, the following barriers hinder the widespread adoption and optimal use of telemedicine devices:
1. Technical Barriers
Successful telemedicine implementation relies on high-speed internet and compatible devices such as smartphones with cameras. Basic technical knowledge of using mobile apps and medical tools is essential for effective telehealth services. Without these factors, telemedicine devices may not function as intended, resulting in service disruptions and reduced care quality.
To overcome these barriers, healthcare providers can offer training programs for both patients and staff on using telemedicine devices and applications. Additionally, investing in reliable internet infrastructure and ensuring that devices meet high standards of compatibility can improve the accessibility and efficiency of remote consultations.
2. Inadequate Reimbursement Policies
Insurance coverage for telemedicine visits remains inconsistent, limiting adoption. While policies are evolving to include telehealth services, reimbursement disparities still pose challenges for providers. Equal compensation for virtual and in-person consultations is crucial for wider acceptance.
One solution is to advocate for policy changes at the legislative level, pushing for uniform reimbursement rates for both virtual and in-person consultations. Healthcare providers can also explore alternative payment models, such as subscription-based services, that reduce dependence on traditional insurance reimbursements.

3. Limited Physical Examination Capabilities
Virtual consultations often restrict thorough physical assessments. Enhancements like improved lighting and supplementary tools, such as flashlights, partially address this limitation. However, certain diagnostic requirements still necessitate in-person evaluations.
Telemedicine devices can be enhanced with supplementary remote diagnostic tools, such as digital stethoscopes or otoscopes, that provide more detailed information. Additionally, combining virtual visits with in-person follow-up appointments or hybrid models of care can address the limitations of physical assessments and ensure comprehensive care.
4. Infrastructure Gaps
Access to essential medical tools, such as thermometers or blood pressure monitors, is necessary for accurate assessments. Faulty or incomplete equipment can lead to errors in clinical decisions, hindering telemedicine effectiveness.
Ensuring that patients have access to high-quality, reliable medical devices is key to overcoming this challenge. Healthcare organizations can provide patients with affordable or subsidized telemedicine kits that include the necessary diagnostic tools, helping to bridge the infrastructure gap for remote care.
5. Patient Data Security Concerns
Data breaches remain a significant risk in telehealth services. Devices that comply with stringent security standards and incorporate advanced encryption protect sensitive patient information. Educating patients on secure usage practices further mitigates risks.
To address security concerns, telemedicine devices must adhere to rigorous security standards, including end-to-end encryption and compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA. Additionally, educating patients on best practices for secure device usage, such as regularly updating passwords and ensuring secure internet connections, can help minimize risks of data breaches.
Implement Your Custom Telemedicine Devices with KMS Healthcare
Telemedicine devices are revolutionizing healthcare by facilitating real-time virtual consultations, enabling continuous remote monitoring of chronic conditions, and streamlining the management of patient care through data-driven insights. KMS Healthcare specializes in integrating telemedicine devices with existing platforms and developing custom software solutions tailored to healthcare organizations:
- Platform Integration: Enable smooth integration between telemedicine devices and existing healthcare systems for streamlined workflows.
- Custom Software Development: Create tailored software to power telemedicine devices and ensure seamless functionality.
- Compliance and Security: Ensure telemedicine solutions adhere to regulatory standards and maintain strict data protection.
Partner with KMS Healthcare to seamlessly integrate telemedicine devices into your systems and optimize implementation.